The Difference Between Rigid, Flexible, and Rigid-Flex PCB Assemblies
 A printed circuit board, or PCB, is a device that uses discrete wiring to connect various electrical components together into a single unit. There are three types of PCB: rigid, flex, and rigid-flex. While each of these options serves the same overall function, they feature some differences in their construction, properties, and design. In this blog, we will identify and discuss how these boards differ.
A printed circuit board, or PCB, is a device that uses discrete wiring to connect various electrical components together into a single unit. There are three types of PCB: rigid, flex, and rigid-flex. While each of these options serves the same overall function, they feature some differences in their construction, properties, and design. In this blog, we will identify and discuss how these boards differ.
Rigid PCB vs. Flex PCB
Rigid PCBs and flexible PCBs fulfill the same basic purpose but feature many differences. Flexible PCBs typically have higher price points than rigid PCBs, as they are able to bend in order to fit the desired application. Flex PCBs are also able to flex without failing for hundreds of thousands of cycles. In addition to their differences in price and flexibility, the following factors differentiate rigid and flex PCBs:
Manufacturing Process
Rigid PCBs utilize a solder mask during the manufacturing process. In contrast, the manufacturing process for flexible PCBs typically includes an overlay or cover-layer. This is necessary to ensure that the board’s exposed circuitry remains protected.
Material
The strength and thickness of rigid PCBs typically come from glass, which serves to reinforce the board. Flexible PCBs do not offer the same levels of strength, but rather utilize a more flexible base material, such as polyimide.
Durability
Although both styles of PCB offer decent amounts of durability, this durability manifests differently for each. Rigid PCBs offer higher levels of strength, while flexible PCBs are better able to absorb vibrations and other shocks.
Weight
Their strength and thickness mean that rigid PCBs weigh slightly more than flexible PCBs, which are typically more lightweight. This is a beneficial property for the electronics industry, which frequently creates small devices that require lighter components.
Resistance
In more extreme environments, flexible PCBs have an advantage over rigid PCBs. Flexible PCBs will generally offer higher levels of resistance to high temperatures. Rigid PCBs, on the other hand, are more prone to becoming damaged or warped.
Sophistication of Design
For more simplistic consumer devices, such as toys or musical keyboards, rigid PCBs typically work very well. However, flexible PCBs are more sophisticated in design, and are thus the ideal choice for highly complex products.
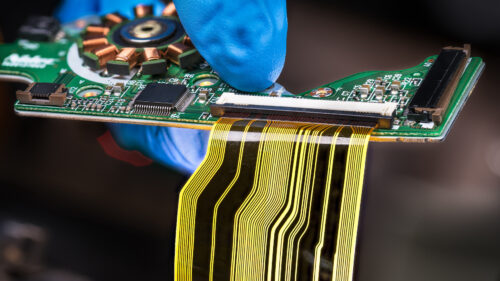 The Rigid-Flex PCB Difference
The Rigid-Flex PCB Difference
The rigid-flex PCB combines the best qualities of rigid and flex PCBs, resulting in a board that is ideal for use across a vast array of industries. It utilizes both rigid and flexible materials, and offers the following advantages:
- Versatility
- Strength
- Stability
- Circuit routing density
By combining the flexibility of flex PCBs with the high strength of rigid PCBs, the rigid-flex PCB works immensely well in complex applications. This type of PCB is highly reliable. It also provides the lightweight benefits of flexible PCBs, and its small size makes it ideal for situations that require a space-saving circuit board.
The many advantages of rigid-flex PCBs mean that this option is typically more expensive than both rigid and flex PCBs. However, it is the ideal choice when one cohesive, reliable solution is needed for sophisticated products.

Custom Circuit Board Assemblies from CCK Automations, Inc.
At CCK Automations, Inc., our experts design custom circuit board assemblies that are uniquely tailored to the specific needs of each customer. We are dedicated to continually meeting our customers’ injection molded plastics and electrical needs. To learn more about our PCB solutions, contact us today.
